As the world accelerates towards a sustainable future, understanding carbon intensity (CI) scores is more crucial than ever. These scores assess the life cycle greenhouse gas emissions associated with various fuel and energy sources, helping industries make informed choices that align with climate goals. In this post, we’ll explore the GREET model for renewable diesel, and three programs and standards for sustainable aviation fuel: CORSIA, IRA’s Section 40B, and RED. We’ll also dive into the potential of ZeaKal’s PhotoSeed soybeans to lower CI scores under these programs.
1. GREET (Greenhouse Gases, Regulated Emissions, and Energy Use in Technologies)
What is the GREET model?
The GREET model, developed by Argonne National Laboratory, is a comprehensive tool for evaluating the lifecycle energy and environmental effects of a wide variety of fuels and vehicle technologies for all transportation sectors, including road, air, marine, and rail. Its primary goal is to provide a transparent, science-based methodology to evaluate the energy and environmental performance of technologies targeting energy efficiency, affordability, and sustainability.
Importance for energy and agriculture
GREET’s emphasis on lifecycle analysis ensures that stakeholders are aware of both immediate and longer term impacts of fuel production and consumption from “well to wheel”. This can be helpful in identifying opportunities to reduce emissions throughout technology development or deployment. GREET, and variations of the model, are used and accepted under several global standards.
The PhotoSeed Impact
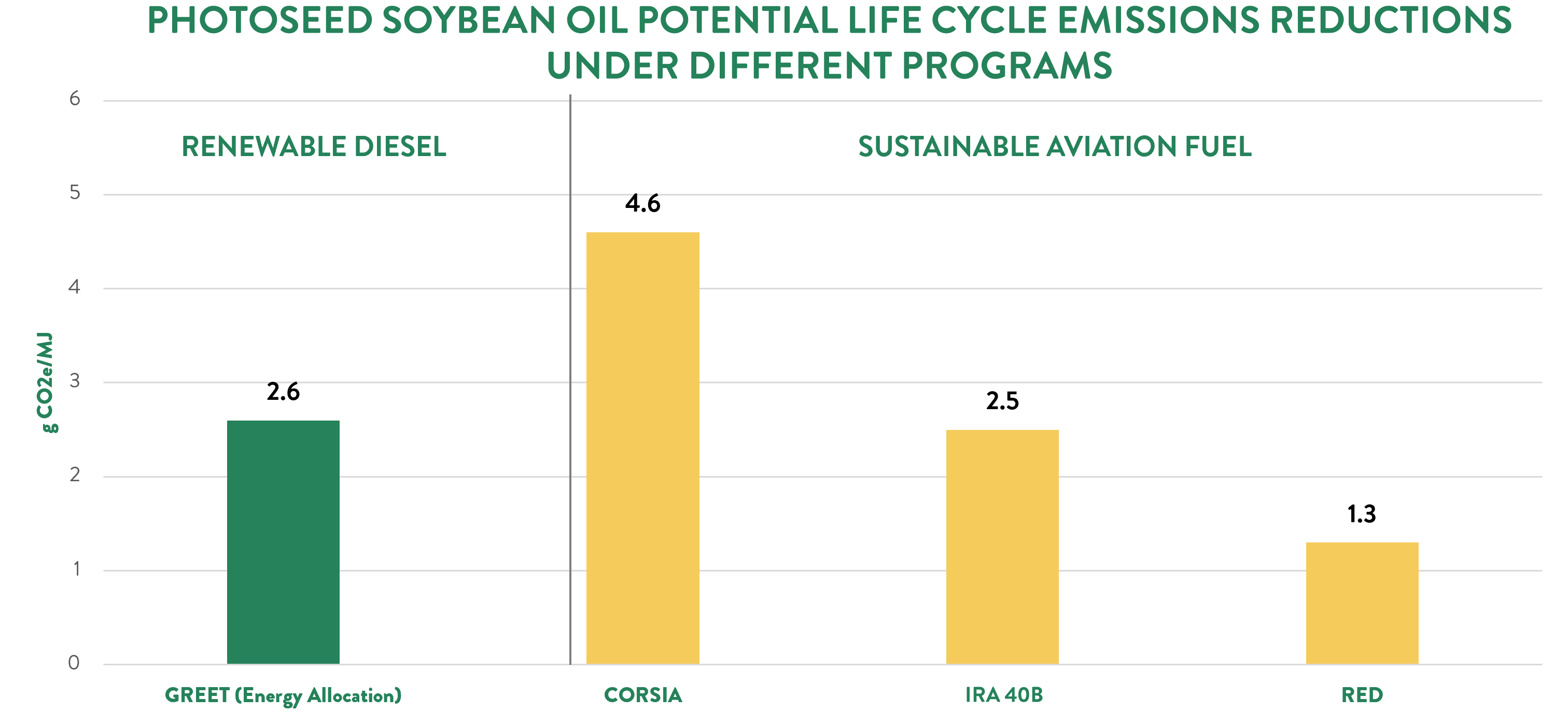
The GREET model suggests that PhotoSeed soy can reduce CI scores by up to 2.6 points (grams of carbon dioxide equivalent per megajoule).
2. CORSIA (Carbon Offsetting and Reduction Scheme for International Aviation)
What is CORSIA?
Importance for energy and agriculture
By setting a clear, international framework for carbon offsetting, CORSIA helps ensure that the aviation sector contributes to global climate goals. Options to decarbonize sustainable aviation fuels (SAF) are currently limited, and agriculture is poised to play an important role.
The PhotoSeed Impact
PhotoSeed has been analyzed to reduce CORSIA CI scores by up to 4.6 points (grams of carbon dioxide equivalent per megajoule).
3. Inflation Reduction Act 40B (IRA 40B)
What is IRA 40B?
The Inflation Reduction Act (IRA) introduced numerous provisions aimed at reducing greenhouse gas emissions across various sectors. One of its key components is Section 40B, which provides incentives for the production and use of sustainable aviation fuels. Incentives are particularly greater for the adoption of technologies and practices proven to reduce carbon intensity scores. IRA 40B establishes a tax credit system for SAF production, encouraging airlines and producers to invest in fuels with lower carbon intensities. This program is designed to accelerate the transition to SAF by financially supporting the development of these fuels.
Importance for energy and agriculture
By providing direct financial incentives, IRA 40B significantly boosts the economic viability of SAF, stimulating innovation and growth within the energy and agriculture sectors producing these fuels and making it an essential tool in the fight against climate change. This policy instrument has the potential to create new revenue streams for farmers looking to move away from a single-commodity market.
The PhotoSeed Impact
Independent analysis demonstrates that under the 40B SAF-GREET model, an aviation fuel-specific modified version of GREET, PhotoSeed reduces CI scores by up to 2.5 points (grams of carbon dioxide equivalent per megajoule).
4. Renewable Energy Directive (RED)
What is the Renewable energy directive?
The Renewable Energy Directive (RED) is a European Union (EU) initiative aimed at promoting renewable energy sources and reducing greenhouse gas emissions across the EU. It sets binding targets for renewable energy use, emphasizing sustainability and carbon reduction. Under RED, sustainable aviation fuels must meet strict sustainability criteria, ensuring they contribute to a significant reduction in greenhouse gas emissions compared to fossil fuels. The directive includes provisions for lifecycle analysis, similar to GREET, to evaluate the carbon intensity of SAFs.
Importance for energy and agriculture
RED plays a crucial role in shaping the future of aviation fuels in Europe. By mandating sustainability criteria and promoting lower carbon intensity fuels, it helps the EU meet its climate targets while encouraging innovation in the renewable energy sector.
The PhotoSeed Impact
PhotoSeed has been analyzed to reduce RED CI scores by up to 1.3 points (grams of carbon dioxide equivalent per megajoule).
Conclusion
Understanding the various global carbon intensity score programs and standards is essential for fueling a sustainable future. Currently, the cost and scale for renewable fuels production falls short of petrochemicals. PhotoSeed leverages plant genetics to capture carbon and expand the volume of global oil production without needing new land or infrastructure. ZeaKal’s genetics and agricultural partnerships offer the energy industry economically feasible feedstocks with improved CI features in the production of SAF and other renewable fuels. We appreciate Foxley, LLC for their independent analysis of PhotoSeed’s impact on CI scores, and SCS Global Services for reviewing the data.
